A Merger of Two Firms May Increase Economic Efficiency by
The direction of price changes will indicate which of these two effects dominates. Demand is sometimes decreasing and internal expansion would result in further price reductions that make the expansion.
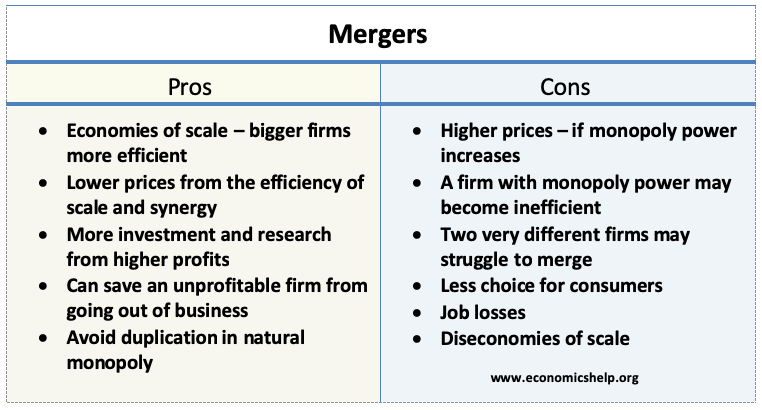
Benefits Of Mergers Economics Help
By agreeing to merge the two firms will join the trend for big European airlines to get bigger.
. For an official signed copy please contact the Antitrust Documents Group. By foreclosing or disadvantaging competing firms vertical restraints create barriers to entry or expansion so that rivals can no longer discipline the offending firms price increases. These are addressed in turn below.
A merger of two firms may increase economic efficiency by A decreasing average total cost through an increase in economies of scale B decreasing output to reduce marginal cost and equalize price C increasing economic profits but decreasing consumer surplus D increasing consumer surplus by decreasing economic profits E increasing consumer surplus by shifting. We also dont find evidence that merged firms are more likely to close down less-efficient plants. The estimated price increases might be considered relatively modest as they are typically between 3 and 7.
Mergers are the result of two firms joining together. Embraced the idea that a mergers economic efficiency ought to be. By gaining a larger market share the new company will be able to gain economies of scale and become more profitable.
However given the large amount of commerce in these industries the implied transfer from consumers to. This document is available in three formats. Hence the introduction of joint dominance makes it more natural to consider efficiencies today.
By combining business activities overall performance efficiency tends to increase and across-the-board costs tend to drop due to the fact that each company leverages off of the other companys. One can expect greater market power to result from the proposed merger of two or more firms in such a market. Economic theory suggests that cost savings and other efficiencies are more likely to dominate the anti-competitive effects of a merger the lower is concentration.
The main motive of any Merger and Acquisitions MA synergy achievement of economies of scale and scope increased market power and revenue growth improvement of managerial efficiency. 7 effective its advertising and promotions will be12although economies of scale can often be achieved through internal expansion and reorganization merger is advantageous because merger is faster than internal expansion. Severin Borenstein 1990 has studied the effect on airfares of two airline mergers.
Whether this raises real competitive concerns depends upon the level of the post-merger. Some mergers may be substantially 1 ikely to raise market power yet also offer a significant possibility of yielding important efficiencies. A merger of two firms may increase economic efficiency by A decreasing average total cost through an increase in economies of scale B decreasing output to reduce marginal cost and equalize price C increasing economic profits but decreasing consumer surplus D increasing consumer surplus by decreasing economic profits.
Synergies occur when two companies with similar businesses combine as they can then consolidate or eliminate duplicate. Incorporating efficiency analysis in merger control. As a result of the merger there will be fewer competitors and consumers may pay more.
In economics market concentration is a function of the number of firms and their respective shares of the total production alternatively total capacity or total reserves in a marketThe market concentration ratio measures the concentration of the top firms in the market this can be through various metrics such as sales employment numbers active users or other relevant. To view the PDF you will need Acrobat Reader which may be downloaded from the Adobe site. This year are estimated to be 176 billion.
Companies also merge to take advantage of synergies and economies of scale. We accordingly analyze vertical restraints in two categories -- those that can lead to collusion and those that can lead to exclusion. Just as powerful firms may use their clout to overcharge customers they can also manipulate markets to pay lower wages.
This paper shows that the Debreu 1951-Farrell 1957 type index suggested by Fare 1986 to calculate the gain in efficiency from merger of firms can be related to a concentration formula. 1968 Merger Guidelines. We have already presented the case that until recently.
Efficiency which may decrease airfares and the exercise of increased market power which may increase airfares. This web page for browsing content PDF comparable to original document formatting and WordPerfect. Recent developments in economics may make an efficiency defence more tractable.
Is it true that the four-firm concentration ratio puts more emphasis on one or two very large firms while the Herfindahl-Hirschman Index puts more. Baumol Panzar and Willig 1982 introduced the idea that there may be efficiency gain from merger of two or more firms. As demonstrated by Williamson 1968 a horizontal merger or acquisition may increase economic efficiency if it allows for the exploitation of previously unutilized economies and scale and scope which may well be greater than the efficiency loses incurred by the merged firms increased market power.
By contrast we find substantial average increases in. The TWA-Ozark and Northwest-Republic mergers. Mergers may provide the acquiring.
In particular economic literature has pointed to the impact of internal cost savings on market power the external output effects of mergers on welfare and the potential destabilising effects merger efficiencies may have for coordinated behavior. Is it true that a merger between two firms that are not already in the top four by size can affect both the four-firm concentration ratio and the Herfindahl-Hirschman Index. There are a number of practical reasons however why internal expansion or contraction sometimes may be a significantly costlier means than merger to increase a firms productive efficiency.
184 First mergers may hasten the speed with which firms can expand their scale to exploit economies of large scale production. With both increased market power and reduced costs net effects on price and on economic efficiency are ambiguous. HHI in merger analysis has a well founded theoretical motivation for homogenous good industries with each firm producing only one good.
This has become an attractive means to make substantial cost savings as they compete against low-cost rivals and try to cope with a dramatic fall in numbers of the profit-making business passengers. Our empirical results indicate that four of the five mergers we study resulted in some increases in some consumer prices.
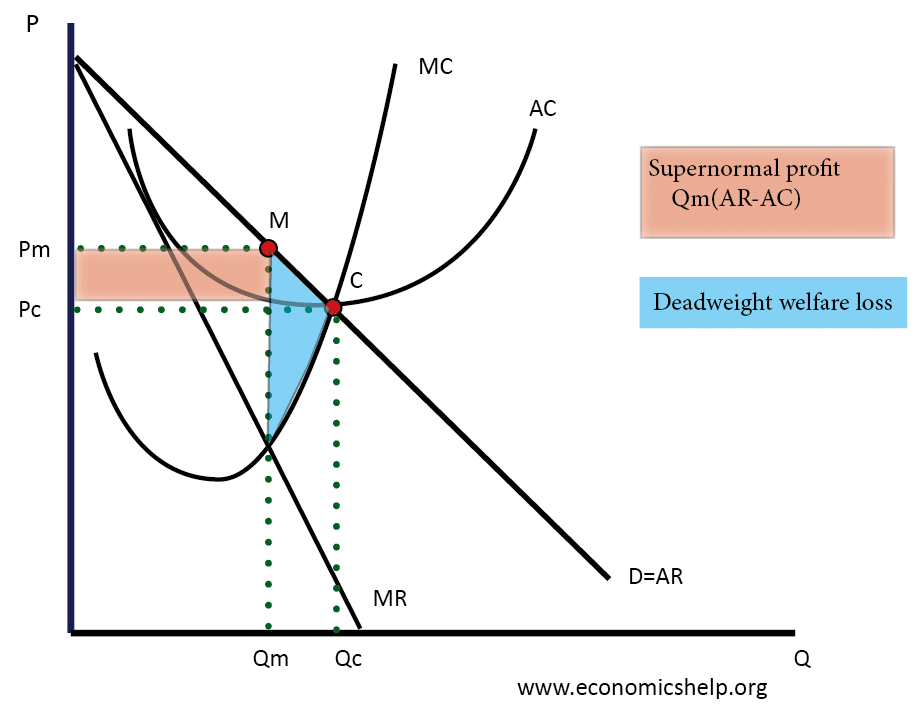
Discuss Whether An Increase In The Market Concentration Ratio Of An Industry Reduces Economic Efficiency Economics Help
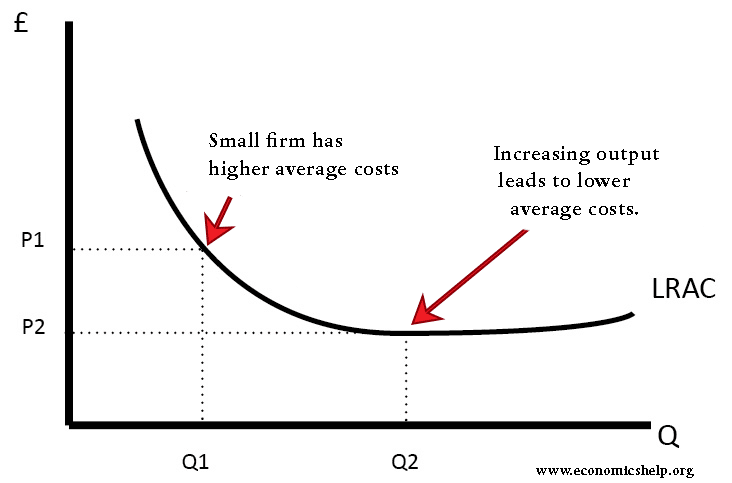
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/MinimumEfficientScaleMES2-c9372fffba0a4a1ab4ab0175600afdb6.png)
No comments for "A Merger of Two Firms May Increase Economic Efficiency by"
Post a Comment